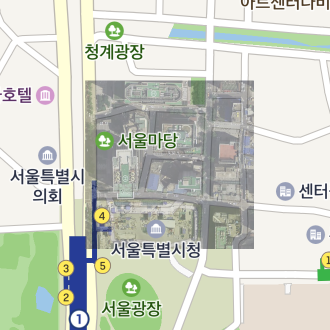
Ground Overlay
A ground overlay shows an image of a specific area on the map. Unlike markers, ground overlays are fixed to areas on the map, and they are zoomed in or out depending on the camera’s movements.
Add and remove ground overlays
A GroundOverlay object can be created just like a general Java object. Create an object, set an area in the bounds property, an image in the image property, and a map object in the map property to add a ground overlay. Note that you should specify the bounds and image properties before specifying the map property; otherwise an exception occurs.
The following code example creates a ground overlay object and adds it to the map.
GroundOverlay groundOverlay = new GroundOverlay();
groundOverlay.setBounds(new LatLngBounds(
new LatLng(37.566351, 126.977234), new LatLng(37.568528, 126.979980)));
groundOverlay.setImage(
OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.ground_overlay_image));
groundOverlay.setMap(naverMap);
Java
GroundOverlay groundOverlay = new GroundOverlay();
groundOverlay.setBounds(new LatLngBounds(
new LatLng(37.566351, 126.977234), new LatLng(37.568528, 126.979980)));
groundOverlay.setImage(
OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.ground_overlay_image));
groundOverlay.setMap(naverMap);
Kotlin
val groundOverlay = GroundOverlay()
groundOverlay.bounds = LatLngBounds(
LatLng(37.566351, 126.977234),
LatLng(37.568528, 126.979980)
)
groundOverlay.setImage(
OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.ground_overlay_image)
)
groundOverlay.map = naverMap
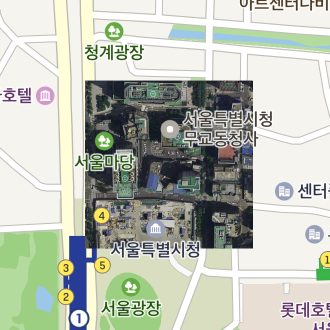
Set the map property to null, and the ground overlay disappears from the map.
The following code example removes a ground overlay from the map.
groundOverlay.setMap(null);
Java
groundOverlay.setMap(null);
Kotlin
groundOverlay.map = null
Bounds
The bounds property specifies the bounds of a ground overlay. This property is required; if you add a ground overlay with no bounds specified to the map, an exception occurs.
The following code example specifies the bounds for a ground overlay.
groundOverlay.setBounds(new LatLngBounds(
new LatLng(37.566351, 126.977234), new LatLng(37.568528, 126.979980)));
Java
groundOverlay.setBounds(new LatLngBounds(
new LatLng(37.566351, 126.977234), new LatLng(37.568528, 126.979980)));
Kotlin
groundOverlay.bounds = LatLngBounds(
LatLng(37.566351, 126.977234),
LatLng(37.568528, 126.979980)
)
Image
The image property specifies an image for a ground overlay. Before specifying an image, you should create an OverlayImage object. OverlayImage is a class that represents bitmap images that can be used by overlays. Using the factory methods defined in this class, you can create an instance from resources, assets, bitmaps and views. As the size of a ground overlay on the screen changes depending on the zoom level, use the nodpi resources or assets irrelevant to user devices’ dots per inch (DPI).
The following code example specifies an image for a ground overlay.
groundOverlay.setImage(
OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.ground_overlay_image));
Java
groundOverlay.setImage(
OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.ground_overlay_image));
Kotlin
groundOverlay.setImage(
OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.ground_overlay_image)
)
Opacity
The alpha property specifies opacity of a ground overlay. The value ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 is fully transparent and 1 is fully opaque. Even though the alpha property is 0, the subjects are still considered to be on the screen, unlike the case where the visible is false. Therefore, they can receive events.
The following code example sets a ground overlay to be semitransparent.
groundOverlay.setAlpha(0.5f);
Java
groundOverlay.setAlpha(0.5f);
Kotlin
groundOverlay.alpha = 0.5f