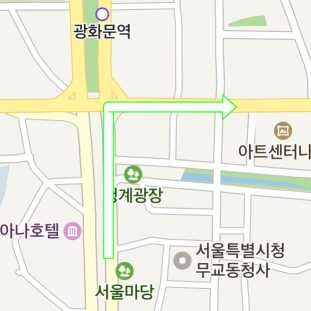
Path and Arrow
The NAVER Maps SDK provides overlays specialized in the navigation service, such as paths and arrows.
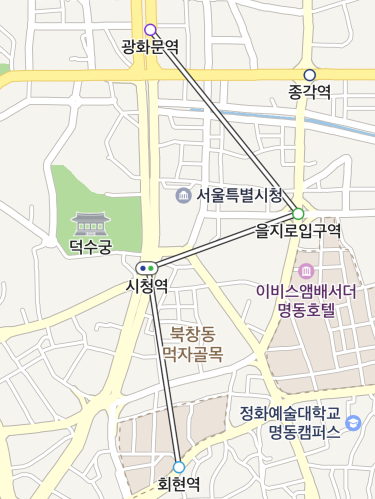
Path overlays
PathOverlay is an overlay that shows paths. It is similar to PolylineOverlay, which also draws a line, but has features specific to paths. PathOverlay allows you to specify a stroke and pattern image, and the width of a path overlay remains the same even if the map is tilted. The stroke and pattern of a path overlay are drawn naturally even if path self-intersection occurs. It also enables you to specify progress, and change the color and stroke of the path depending on the progress.
Add and remove path overlays
A path overlay can be created just like a general Java object. Create an object, set a list of coordinates in the coords property and set a map object in the map property to add a path overlay. Note that you should specify the coords property before specifying the map property; otherwise an exception occurs.
The following code example creates a path overlay object and adds it to the map.
PathOverlay path = new PathOverlay();
path.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
));
path.setMap(naverMap);
Java
PathOverlay path = new PathOverlay();
path.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
));
path.setMap(naverMap);
Kotlin
val path = PathOverlay()
path.coords = listOf(
LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
path.map = naverMap
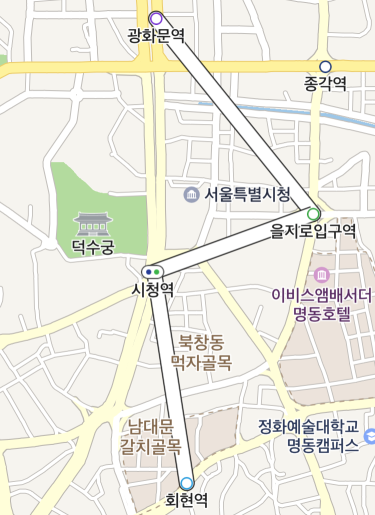
Set the map property to null, and the path overlay disappears from the map.
The following code example removes a path overlay from the map.
List of coordinates
The coords property specifies a list of coordinates. This property is required; if you add a path overlay with no list of coordinates to the map, an exception occurs. Also, if the list of coordinates is less than 2 in size or has null, an exception occurs.
The following code example specifies a list of coordinates for a path overlay.
path.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
));
Java
path.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
));
Kotlin
path.coords = listOf(
LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
Even if you change the coordinates object specified in the coords property or the one obtained with the property, the changes are not applied. To apply the changes, the changed coordinates object should be set in the coords property again.
The following code example changes part of the list of coordinates of a path overlay.
List<LatLng> coords = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coords,
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
);
path.setCoords(coords);
coords.set(0, new LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335));
// Not yet reflected
path.setCoords(coords);
// Reflected
Java
List<LatLng> coords = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coords,
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
);
path.setCoords(coords);
coords.set(0, new LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335));
// Not yet reflected
path.setCoords(coords);
// Reflected
Kotlin
val coords = mutableListOf(
LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
path.coords = coords
coords[0] = LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335)
// Not yet reflected
path.coords = coords
// Reflected
Width
The width property specifies the stroke width of a polyline.
The following code example sets the width of a path overlay to 30 px.
Stroke width
The outlineWidth property specifies the stroke width of a circle overlay. Set the property to 0 to draw no outline.
The following code example sets the stroke width of a path overlay to 5 px.
Pattern
A pattern is an image that is regularly repeated along the path overlay. It is useful to express the direction of a path.
The patternImage property specifies a pattern image. Set this property to null, and no pattern is drawn. Before specifying a pattern image, you should create an OverlayImage object. OverlayImage is a class that represents bitmap images that can be used by overlays. Using the factory methods defined in this class, you can create an instance from resources, assets, bitmaps and views. As pattern images should be handled depending on user devices’ dots per inch (DPI), using Drawable resources is recommended.
The patternInterval property specifies the interval between pattern images. Set this property to 0, and no pattern is drawn.
The following code example specifies a pattern image for a path overlay and sets the interval to 10 px.
path.setPatternImage(OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.path_pattern));
path.setPatternInterval(10);
Java
path.setPatternImage(OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.path_pattern));
path.setPatternInterval(10);
Kotlin
path.patternImage = OverlayImage.fromResource(R.drawable.path_pattern)
path.patternInterval = 10
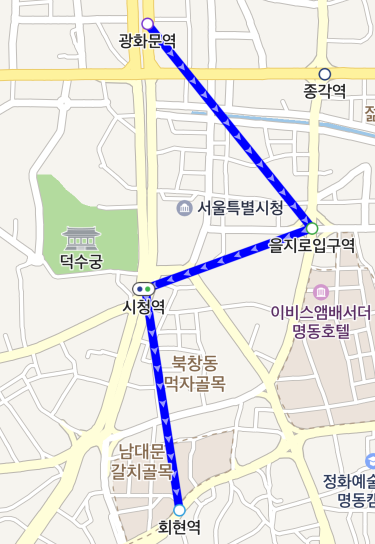
Progress
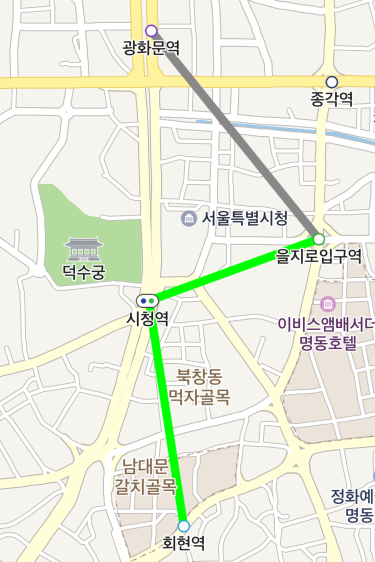
The progress property specifies progress. The value can range from 0 to 1, where 0 is the starting point, and 1 is the destination. As you can specify different colors for the path that has been traveled and the one to be traveled, you do not need to change the list of coordinates to apply the progress.
The following code example sets the progress of a path overlay to 50 %.
Fill color
The color and passedColor properties specify colors for the path to be traveled and the one that has been traveled, respectively.
The following code example sets the color of the path to be traveled to green, and the one that has been traveled to gray.
path.setColor(Color.GREEN);
path.setPassedColor(Color.GRAY);
Java
path.setColor(Color.GREEN);
path.setPassedColor(Color.GRAY);
Kotlin
path.color = Color.GREEN
path.passedColor = Color.GRAY
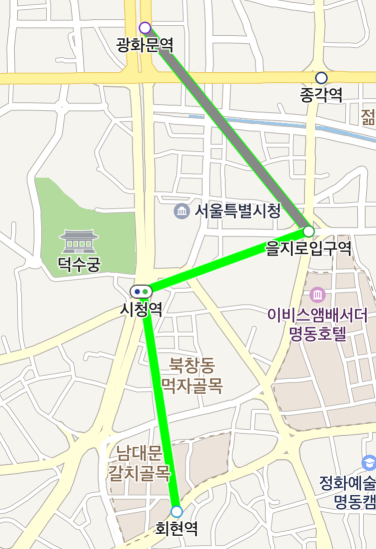
Stroke color
The outlineColor and passedOutlineColor properties specify stroke colors for the path to be traveled and the one that has been traveled, respectively.
The following code example sets the stroke color of the path to be traveled to white, and the one that has been traveled to green.
path.setOutlineColor(Color.WHITE);
path.setPassedOutlineColor(Color.GREEN);
Java
path.setOutlineColor(Color.WHITE);
path.setPassedOutlineColor(Color.GREEN);
Kotlin
path.outlineColor = Color.WHITE
path.passedOutlineColor = Color.GREEN
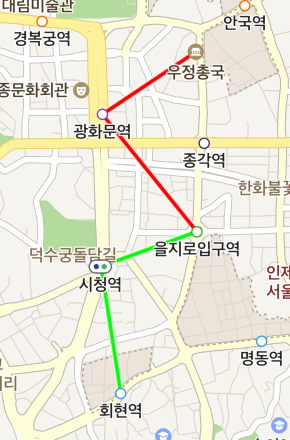
Multipart path overlays
MultipartPathOverlay is a special path overlay that specifies different colors for a path overlay in parts. It is easy and efficient to use a multipart path overlay to draw a path with multiple colors, rather than using multiple path overlays.
Add and remove multipart path overlays
A multipart path overlay can be created just like a general Java object. Create an object, set a list of coordinates in the coordParts property, and a list of colors in the colorParts property, and set a map object in the map property to draw a multipart path overlay. Note that you should specify the coordParts and colorParts properties before specifying the map property; if you do not specify them or the two parts are different in size, an exception occurs.
The following code example creates a multipart path overlay object and adds it to the map.
MultipartPathOverlay multipartPath = new MultipartPathOverlay();
multipartPath.setCoordParts(Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
));
multipartPath.setColorParts(Arrays.asList(
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.GRAY, Color.LTGRAY),
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.GREEN, Color.WHITE, Color.DKGRAY, Color.LTGRAY)
));
multipartPath.setMap(naverMap);
Java
MultipartPathOverlay multipartPath = new MultipartPathOverlay();
multipartPath.setCoordParts(Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
));
multipartPath.setColorParts(Arrays.asList(
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.GRAY, Color.LTGRAY),
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.GREEN, Color.WHITE, Color.DKGRAY, Color.LTGRAY)
));
multipartPath.setMap(naverMap);
Kotlin
val multipartPath = MultipartPathOverlay()
multipartPath.coordParts = listOf(
listOf(
LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
listOf(
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
)
multipartPath.colorParts = listOf(
MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED,
Color.WHITE,
Color.GRAY,
Color.LTGRAY
),
MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.GREEN,
Color.WHITE,
Color.DKGRAY,
Color.LTGRAY
)
)
multipartPath.map = naverMap
The following code example removes a multipart path overlay from the map.
multipartPath.setMap(null);
Java
multipartPath.setMap(null);
Kotlin
multipartPath.map = null
Coordinates part
The coordParts property specifies a list of coordinates. This property is required; if you add a multipart path overlay with no list of coordinates to the map, an exception occurs. The coordParts is expressed as a two dimensional list of coordinates. The list must have at least one part. Otherwise, an exception occurs. Also, if each coordinates part is less than 2 in size or has null, an exception occurs.
The following code example specifies two coordinates parts for a multipart path overlay.
multipartPath.setCoordParts(Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
));
Java
multipartPath.setCoordParts(Arrays.asList(
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
));
Kotlin
multipartPath.coordParts = listOf(
listOf(
LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
listOf(
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
)
Even if you change the coordinates object specified in the coordParts property or the one obtained with the property, the changes are not applied. To apply the changes, the changed coordinates object should be set in the coordParts property again.
The following code example changes part of the list of coordinates of a multipart path overlay.
List<LatLng> coordPart1 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coordPart1,
new LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
);
List<LatLng> coordPart2 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coordPart2,
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
);
List<List<LatLng>> coordParts = Arrays.asList(coordPart1, coordPart2);
multipartPath.setCoordParts(coordParts);
coordParts.get(0).set(0, new LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335));
// Not yet reflected
multipartPath.setCoordParts(coordParts);
// Reflected
Java
List<LatLng> coordPart1 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coordPart1,
new LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
new LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
);
List<LatLng> coordPart2 = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coordPart2,
new LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
new LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
new LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
);
List<List<LatLng>> coordParts = Arrays.asList(coordPart1, coordPart2);
multipartPath.setCoordParts(coordParts);
coordParts.get(0).set(0, new LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335));
// Not yet reflected
multipartPath.setCoordParts(coordParts);
// Reflected
Kotlin
val coordParts = mutableListOf(
mutableListOf(
LatLng(37.5744287, 126.982625),
LatLng(37.57152, 126.97714),
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268)
),
mutableListOf(
LatLng(37.56607, 126.98268),
LatLng(37.56445, 126.97707),
LatLng(37.55855, 126.97822)
)
)
multipartPath.coordParts = coordParts
coordParts[0][0] = LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335)
// Not yet reflected
multipartPath.coordParts = coordParts
// Reflected
Color part
The colorParts property specifies a list of colors. To specify color parts, you should create a MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart object. ColorPart is a class that represents information of colors to assign for each coordinates part. It allows you to specify the fill color and stroke color for the path to be traveled and the one that has been traveled, respectively.
The following code example creates a MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart object.
MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart colorPart = new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, // Set the color of the path to be traveled to red.
Color.WHITE, // Set the stroke color of the path to be traveled to white.
Color.GRAY, // Set the color of the path that has been traveled to gray.
Color.LTGRAY // Set the stroke color of the path that has been traveled
// to light gray.
);
Java
MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart colorPart = new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, // Set the color of the path to be traveled to red.
Color.WHITE, // Set the stroke color of the path to be traveled to white.
Color.GRAY, // Set the color of the path that has been traveled to gray.
Color.LTGRAY // Set the stroke color of the path that has been traveled
// to light gray.
);
Kotlin
val colorPart = MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, // Set the color of the path to be traveled to red.
Color.WHITE, // Set the stroke color of the path to be traveled to white.
Color.GRAY, // Set the color of the path that has been traveled to gray.
Color.LTGRAY // Set the stroke color of the path that has been traveled
// to light gray.
)
Set a ColorPart list in the colorParts property, and the colors are reflected. Each part of colorParts corresponds to that in coordParts. That is, the color of index 0 in the coordinates part is specified as the value of index 0 in the color part. Therefore, the coordParts property must be specified, and it must be the same as the colorParts property in size. Otherwise, an exception occurs when you add a multipart path overlay to the map. An exception also occurs when the list has an element that is null.
The following code example specifies two color parts for a multipart path overlay.
multipartPath.setColorParts(Arrays.asList(
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.GRAY, Color.LTGRAY),
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.GREEN, Color.WHITE, Color.DKGRAY, Color.LTGRAY)
));
Java
multipartPath.setColorParts(Arrays.asList(
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED, Color.WHITE, Color.GRAY, Color.LTGRAY),
new MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.GREEN, Color.WHITE, Color.DKGRAY, Color.LTGRAY)
));
Kotlin
multipartPath.colorParts = listOf(
MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.RED,
Color.WHITE,
Color.GRAY,
Color.LTGRAY
),
MultipartPathOverlay.ColorPart(
Color.GREEN,
Color.WHITE,
Color.DKGRAY,
Color.LTGRAY
)
)
Common properties
Multipart path overlays support all the features supported by path overlays. Like path overlays, you can specify the width, stroke width, pattern and progress of multipart path overlays.
Arrowhead path overlay
ArrowheadPathOverlay is an overlay that represents a direction or rotation point with an arrowhead. It represents a list of coordinates like path overlays, but does not specify progress and contains an arrowhead at the end.
Add and remove arrowhead path overlays
An arrowhead path overlay can be created just like a general Java object. Create an object, set a list of coordinates in the coords property and set a map object in the map property to draw an arrowhead path overlay. Note that you should specify the coords property before specifying the map property; otherwise an exception occurs.
The following code example creates an arrowhead path overlay object and adds it to the map.
ArrowheadPathOverlay arrowheadPath = new ArrowheadPathOverlay();
arrowheadPath.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
));
arrowheadPath.setMap(naverMap);
Java
ArrowheadPathOverlay arrowheadPath = new ArrowheadPathOverlay();
arrowheadPath.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
));
arrowheadPath.setMap(naverMap);
Kotlin
val arrowheadPath = ArrowheadPathOverlay()
arrowheadPath.coords = listOf(
LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
)
arrowheadPath.map = naverMap
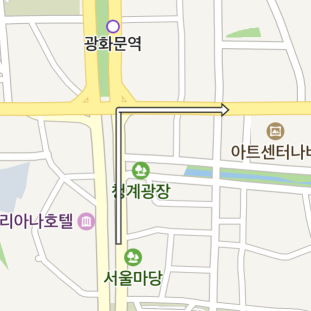
Set the map property to null, and the arrowhead path overlay disappears from the map.
The following code example removes an arrowhead path overlay from the map.
arrowheadPath.setMap(null);
Java
arrowheadPath.setMap(null);
Kotlin
arrowheadPath.map = null
List of coordinates
The coords property specifies a list of coordinates. This property is required; if you add an arrowhead path overlay with no list of coordinates to the map, an exception occurs. Also, if the list of coordinates is less than 2 in size or has null, an exception occurs. An arrowhead symbol is drawn at the last coordinates.
The following code example specifies a list of coordinates for an arrowhead path overlay.
arrowheadPath.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
));
Java
arrowheadPath.setCoords(Arrays.asList(
new LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
));
Kotlin
arrowheadPath.coords = listOf(
LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
)
Even if you change the coordinates object specified in the coords property or the one obtained with the property, the changes are not applied. To apply the changes, the changed coordinates object should be set in the coords property again.
The following code example changes part of the list of coordinates of an arrowhead path overlay.
List<LatLng> coords = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coords,
new LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
);
arrowheadPath.setCoords(coords);
coords.set(0, new LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335));
// Not yet reflected
arrowheadPath.setCoords(coords);
// Reflected
Java
List<LatLng> coords = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(coords,
new LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
new LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
);
arrowheadPath.setCoords(coords);
coords.set(0, new LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335));
// Not yet reflected
arrowheadPath.setCoords(coords);
// Reflected
Kotlin
val coords = mutableListOf(
LatLng(37.568003, 126.9772503),
LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9772503),
LatLng(37.5701573, 126.9793745)
)
arrowheadPath.coords = coords
coords[0] = LatLng(37.5734571, 126.975335)
// Not yet reflected
arrowheadPath.coords = coords
// Reflected
Width
The width property specifies the width of an arrowhead path overlay.
The following code example sets the width of an arrowhead path overlay to 20 px.
arrowheadPath.setWidth(20);
Java
arrowheadPath.setWidth(20);
Kotlin
arrowheadPath.width = 20
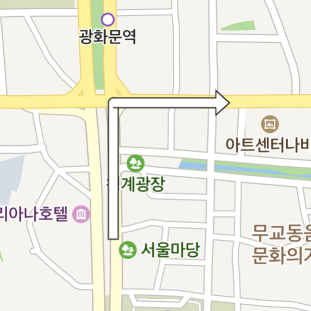
Head size
The headSizeRatio property specifies the ratio of the arrowhead size. The arrowhead size is measured by the width multiplied by the ratio.
The following code example sets the arrowhead size of an arrowhead path overlay to a value 4 times the width.
arrowheadPath.setHeadSizeRatio(4);
Java
arrowheadPath.setHeadSizeRatio(4);
Kotlin
arrowheadPath.headSizeRatio = 4f
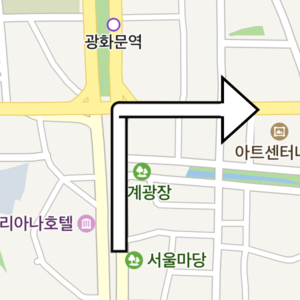
Fill color
The color property specifies the fill color of an arrowhead path overlay.
The following code example sets the color of an arrowhead path overlay to green.
arrowheadPath.setColor(Color.GREEN);
Java
arrowheadPath.setColor(Color.GREEN);
Kotlin
arrowheadPath.color = Color.GREEN
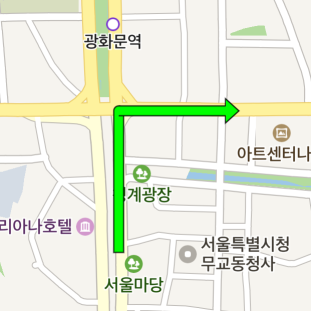
Stroke color
The outlineColor property specifies the stroke color of an arrowhead path overlay.
The following code example sets the stroke color of an arrowhead path overlay to green.
arrowheadPath.setOutlineColor(Color.GREEN);
Java
arrowheadPath.setOutlineColor(Color.GREEN);
Kotlin
arrowheadPath.outlineColor = Color.GREEN